Co Dominance Punnett Square Calculator Examples and Practice Quiz
Scroll down to try our codominance punnett square calculator, explore real-life and practical examples and get a 20-questions quiz as a practice to judge your knowledge about the topic.
Codominance Punnett Square Calculator
Calculate genetic inheritance patterns where both alleles are fully expressed in the phenotype
Parent 1
Gene 1
Gene 2
Gene 3
Parent 2
Gene 1
Gene 2
Gene 3
Phenotype Distribution
Phenotype Distribution
Phenotype Distribution
About Codominance
Codominance is a form of inheritance where both alleles for a gene are fully expressed in the phenotype of heterozygous organisms. Unlike complete dominance where one allele masks the other, or incomplete dominance where a blend occurs, codominance results in both traits being distinctly visible.
Interactive Codominance Demonstration
Flower Color Inheritance
Visual Examples of Codominance
Flower Color Codominance
In this example, red flowers (RR) and white flowers (WW) produce spotted offspring (RW) when crossed. Both red and white traits are expressed simultaneously rather than blending into pink.
Molecular Basis
Each allele codes for different pigment proteins that are independently expressed in the flower petals, creating a spotted pattern rather than mixing to form a new color.
Roan Coat in Cattle
A classic example of codominance in animals is the roan coat pattern in cattle. When a red cow (RR) is crossed with a white cow (WW), the offspring have a roan coat (RW) with red and white hairs intermixed.
Agricultural Significance
Roan cattle are valued in some breeds for their distinctive appearance. The codominant inheritance pattern allows breeders to predict coat colors with high accuracy when planning crosses.
ABO Blood Type System
The classic example of codominance in humans is the ABO blood type system. Type A and Type B are codominant, resulting in Type AB blood when both alleles are present, with both A and B antigens expressed on red blood cells.
Medical Importance
Understanding blood type inheritance is crucial for medical procedures like transfusions and organ transplants. The codominant expression of blood type antigens determines compatibility between donors and recipients.
Examples of codominance include:
- ABO blood types in humans (I^A and I^B alleles)
- Roan coat color in cattle (red and white alleles)
- Spotted or striped patterns in certain flowers
- Feather coloration in some bird species
- Scale patterns in some fish
- Fur color in certain cat breeds
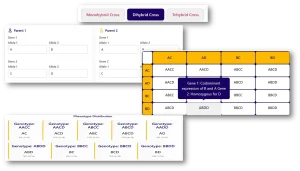
Use this calculator to predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes when codominance is present.
How to Use the Codominance Punnett Square Calculator
Follow these simple steps to perform a codominance punnett square activity on either of Monohybird, Dihybrid or Trihybrid corsses.
1. Select Cross Type
- Choose between Monohybrid, Dihybrid, or Trihybrid cross.
- The appropriate input fields will be displayed based on your selection.
2. Enter Parental Alleles
- Input the alleles for each parent.
- Use uppercase letters to represent codominant alleles (e.g., R and W for coat color, IA and IB for blood type).
3. Generate the Punnett Square
- Click the “Calculate” button to get an answer to how codominance looks like on a Punnett Square.
- The calculator instantly computes genotypic and phenotypic probabilities.
4. Analyze the Results
- Examine the Punnett square grid to see all possible genotype combinations.
- Review the phenotype distribution table to understand expected offspring ratios.
- Hover over results to view detailed explanations of each genetic outcome.
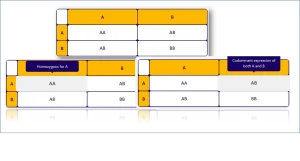
For instance, when you generate a codominant punnett square using a monohybrid cross, a codominance punnett square will look like the following:
Understanding the Results of Calculation
When you use the Codominance Punnett Square Calculator, your results will be displayed in both genotypic and phenotypic formats, helping you analyze inheritance patterns effectively.
Explore our other genetics tools: The Complete Dominance Punnett Square Calculator for dominant-recessive inheritance and the Incomplete Dominance Punnett Square Calculator to visualize blended phenotypes!
Genotype Notation: How to Read the Genetic Codes
The calculator represents genotypes using standardized letter combinations to denote different alleles:

- Uses two-letter combinations (e.g., AA, AB, BB).

- Uses four-letter combinations (e.g., AABB, AaBb, AaBB).

- Uses six-letter combinations (e.g., AABBCc, AaBbCc).

Each letter represents a specific allele, with different capitalizations used to indicate the inheritance pattern. For codominant traits, two different uppercase letters (e.g., A and B) indicate codominance, where both traits are equally expressed in the phenotype.
Phenotype Interpretation: What Do the Results Mean?
In codominance, both alleles are fully expressed, leading to distinct traits appearing simultaneously rather than blending. Here’s how to interpret your results:
- Homozygous Genotypes (e.g., AA or BB) → Express a single dominant phenotype.
- Heterozygous Genotypes (e.g., AB) → Express both parental phenotypes equally in the offspring.
Understanding the Phenotype Distribution Table
The calculator provides a detailed breakdown of phenotype probabilities, including:



This data helps predict genetic outcomes in different breeding experiments, research studies, and classroom applications.
Features of the Codominance Punnett Square Calculator
Our calculator is designed to simplify genetic inheritance analysis with powerful computational tools and interactive features.
1. Multiple Cross Types



2. Visual Representations



3. Phenotypic Analysis



4. Educational Tools & Interactive Learning



5. User-Friendly & Accessible Design



Codominance Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
Test your understanding of codominance inheritance patterns with this 20-question practice quiz. After completion, students can check their result. Users can also download complete practice worksheet in PDF form with correct options for later use.
Quiz Results
Complete the quiz to see your performance analysis.