Primer Dilution Calculator – Accurate Oligo Concentration Tool
Accurately dilute your oligonucleotides in seconds! Use our Oligo Dilution Calculator to get precise primer concentrations for PCR, qPCR, and sequencing—fast, easy, and error-free! 🚀
For research use only. Always verify calculations independently.
🧪 How to Use the Oligo Dilution Calculator?
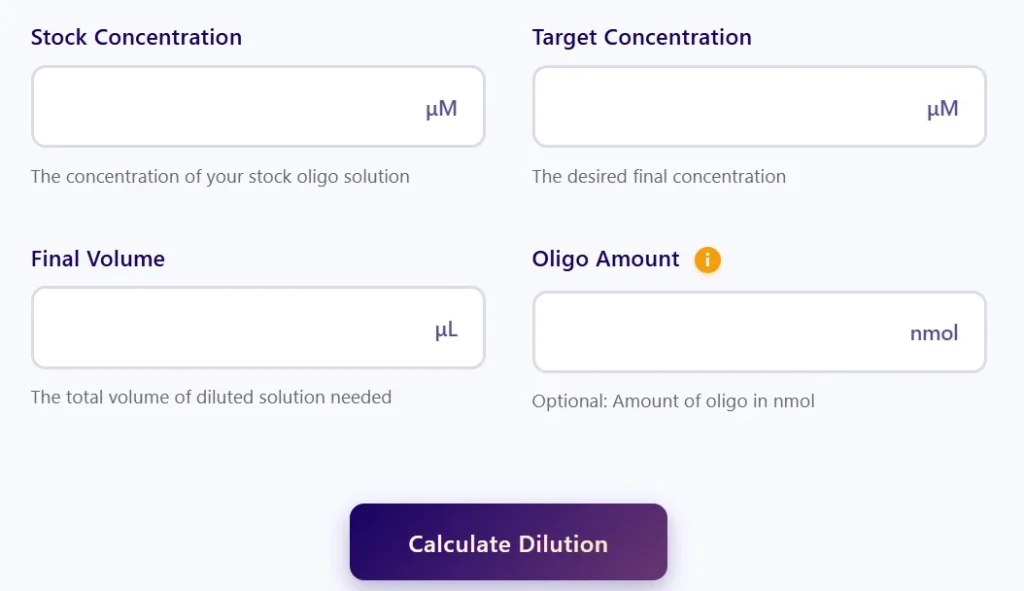
- Enter the stock concentration (e.g., 100 µM)
- Enter the desired final concentration (e.g., 10 µM)
- Enter the final solution volume (e.g., 100 µL)
- Click Calculate to get the required stock and diluent volumes.
How to Accurately Prepare DNA & RNA Oligos
Oligonucleotides (oligos) are short single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules used in a wide range of molecular biology applications, including PCR, qPCR, sequencing, gene synthesis, and CRISPR genome editing. Since these oligos are typically synthesized in a dry, lyophilized form, they must be resuspended and diluted before use.
To ensure accurate and reproducible results, proper oligo dilution is essential. This guide explains:
✅ What oligo dilution is and why it matters
✅ How to use the C1V1 = C2V2 dilution formula
✅ Step-by-step oligo resuspension and dilution
✅ Best practices for storage and handling
Why is Oligo Dilution Important?
Correct dilution ensures that experiments receive the precise amount of oligo needed for reactions such as PCR primer binding, qPCR probe detection, and hybridization assays. Incorrect dilution can lead to:
❌ Failed experiments due to incorrect oligo concentrations
❌ Inconsistent results across different assays
❌ Wasted time and resources from inaccurate reagent preparation
By following a standardized oligo dilution protocol, researchers can maintain accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in their experiments.
Understanding Oligo Concentrations
Oligonucleotides are typically measured in molar concentrations (M, mM, µM, nM) or in mass units (ng/µL, µg/mL, pmol/µL).
🔹 Common Oligo Concentration Units:
| Unit | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Micromolar (µM) | 10⁻⁶ moles per liter | 100 µM oligo stock |
| Nanomolar (nM) | 10⁻⁹ moles per liter | 500 nM qPCR probe |
| Picomoles per microliter (pmol/µL) | 10⁻¹² moles per microliter | 10 pmol/µL stock |
🔹 Stock solutions are usually prepared at high concentrations (e.g., 100 µM) to minimize storage volume.
🔹 Working solutions are diluted to lower concentrations (e.g., 10 µM, 1 µM) for experimental use.
The Oligo Dilution Formula
To calculate how much stock solution and diluent to use, the C1V1 = C2V2 formula is applied:
C1 × V1 = C2 × V2
Where:
- C1 = Initial (stock) concentration (µM)
- V1 = Volume of stock solution needed (µL)
- C2 = Desired (final) concentration (µM)
- V2 = Final total volume (µL)
How to Dilute an Oligo | Guide
Step 1: Determine Your Stock Concentration (C1)
- Check the manufacturer’s datasheet or the oligo resuspension concentration used.
- Most oligos are resuspended at 100 µM or 1 mM stock concentrations.
Step 2: Choose Your Desired Final Concentration (C2)
- For PCR primers, typical concentrations range from 5–10 µM.
- For qPCR probes, working concentrations are often 100–500 nM.
Step 3: Decide the Total Volume Needed (V2)
- This depends on how much solution you need for your experiment (e.g., 100 µL, 500 µL, 1 mL).
Step 4: Apply the Formula C1V1 = C2V2
- Solve for V1, the volume of stock solution required.
- Calculate V1 = (C2 × V2) ÷ C1
Example Oligo Dilution Calculation
🧬 Scenario: You have a 100 µM stock oligo and need to prepare 100 µL of a 10 µM working solution.
✅ Given:
- Stock concentration (C1) = 100 µM
- Final concentration (C2) = 10 µM
- Final volume (V2) = 100 µL
✅ Calculation:
- V1 = (C2 × V2) ÷ C1
- V1 = (10 µM × 100 µL) ÷ 100 µM
- V1 = 10 µL
🧪 Final Steps:
- Pipette 10 µL of stock oligo into a new tube.
- Add 90 µL of nuclease-free water or TE buffer to reach 100 µL total volume.
- Mix gently and store properly.
📌 Result: You now have a 10 µM oligo solution ready for your experiment!
Best Practices for Oligo Dilution & Storage
✔ Use nuclease-free water or TE buffer – Prevents degradation by DNases/RNases.
✔ Store diluted oligos at -20°C to -80°C – Ensures long-term stability.
✔ Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles – Aliquot into small volumes if necessary.
✔ Label tubes properly – Include name, date, concentration, and buffer used.
✔ Vortex and spin down – Ensures uniform mixing before use.
📌 Tip: For long-term storage, resuspend oligos at higher concentrations (e.g., 100 µM) and dilute them right before use.
How to Use This Eye Color Calculator
Q: What is an Oligo Dilution Calculator, and how does it work?
A: An Oligo Dilution Calculator is a tool used to determine the correct volumes of stock oligonucleotide solutions and diluents required to achieve a desired concentration. It uses the C1V1 = C2V2 formula, ensuring accurate oligo preparation for PCR, qPCR, NGS, and cloning.
Q: How do I calculate primer dilution for PCR?
A: To prepare PCR primers at a specific concentration (e.g., 10 µM working solution), use a Primer Dilution Calculator. If your stock primer is at 100 µM, and you need 10 µM in 100 µL, apply:
(100 µM × V1) = (10 µM × 100 µL)
V1 = 10 µL stock primer + 90 µL nuclease-free water
Q: What is a Primer Concentration Calculator?
A: A Primer Concentration Calculator helps determine the molar concentration of a primer solution based on its mass (µg), molecular weight (MW), and volume. The formula is:
Concentration (µM) = (Mass of primer in µg × 10⁶) ÷ (MW × Volume in µL)
This tool ensures accurate preparation of PCR primers, qPCR probes, and sequencing oligos.
Q: How do I use an Oligo Concentration Calculator?
A: An Oligo Concentration Calculator helps convert between mass (ng, µg), molar concentration (µM, nM), and volume (µL, mL). Simply enter:


The calculator instantly provides the correct concentration (µM or nM), useful for oligo resuspension and dilution calculations.
Q: How do I prepare a 100 µM stock solution of an oligo?
A: To make a 100 µM oligo stock solution, dissolve the dry oligonucleotide pellet in an appropriate volume of nuclease-free water or TE buffer.
Volume (µL) = Mass (nmol) × 10
For example, if you receive 50 nmol of an oligo, dissolve it in 500 µL of buffer to create a 100 µM solution.
Q: What is a Concentration Dilution Calculator?
A: A Concentration Dilution Calculator determines how to dilute a high-concentration stock solution to a desired lower concentration. It is useful for oligos, primers, antibodies, and reagents in molecular biology experiments.
Q: How do I store diluted primers and oligos?
A: Store diluted oligonucleotides at:


For RNA oligos (e.g., siRNA, gRNA for CRISPR), store at -80°C for maximum stability.
Q: What diluent should I use for oligonucleotide solutions?
A: The best diluents for oligonucleotide resuspension and dilution are:

For PCR and qPCR applications, nuclease-free water is preferred to avoid buffer interference.
Q: Can I use the same dilution method for RNA and DNA oligos?
A: Yes, but RNA oligos are more sensitive to degradation. Always use RNase-free conditions, store in low-temperature environments, and dilute in RNase-free water or TE buffer.
Q: How do I perform serial dilutions for oligos?
A: Serial dilutions are performed when you need multiple stepwise dilutions (e.g., 100 µM → 10 µM → 1 µM). Use a Serial Dilution Calculator to accurately determine the dilution factor and volumes at each step.
For example:
- Dilute 100 µM stock → Take 10 µL stock + 90 µL buffer → Produces 10 µM solution
- Dilute 10 µM solution → Take 10 µL + 90 µL buffer → Produces 1 µM solution
This method ensures precise primer and probe dilutions for PCR, qPCR, and sequencing workflows.