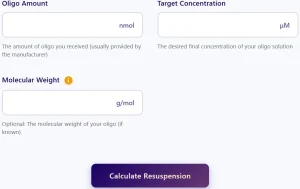
Oligo Resuspension Calculator
Calculate the volume of solvent needed to resuspend your lyophilized oligos to a specific concentration. Enter your parameters below to get accurate results.
For research use only. Always verify calculations independently.
How to Use the Oligo Resuspension Calculator
Follow these steps to accurately resuspend your oligonucleotides and prepare them for experimental applications:
Enter the Oligo Amount
- Input the quantity of the lyophilized oligonucleotide provided by the manufacturer. This value is typically given in nanomoles (nmol) or micrograms (µg).
Specify the Target Concentration
- Define the final concentration at which you need your oligonucleotide stock solution. Standard concentrations include 100 µM for PCR primers and 10 µM for working solutions, but these values can vary depending on the experimental requirements.
Input the Molecular Weight (Optional)
- If known, enter the molecular weight (MW) in g/mol. The molecular weight varies depending on the sequence composition and modifications, impacting the concentration calculations. If left blank, an average MW is used for standard oligonucleotides.
Click “Calculate Resuspension”
- The calculator processes your inputs and determines the exact volume of solvent required to achieve the specified concentration.
Review the Results
- The output provides the resuspension volume in microliters (µL) and the resulting stock concentration in milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL).
By following these steps, students and researchers can efficiently prepare accurate and reproducible oligonucleotide solutions, ensuring precise experimental conditions.
An Introduction to Oligo Resuspension
Oligonucleotide resuspension is a fundamental step in molecular biology, ensuring that synthetic DNA or RNA sequences are dissolved in precise concentrations for experimental applications. Whether you are working with PCR primers, hybridization probes, CRISPR guide RNAs, or other custom oligonucleotides, accurate resuspension is essential for achieving reproducible and reliable results in laboratory workflows.
Lyophilized (freeze-dried) oligonucleotides must be carefully reconstituted in an appropriate solvent to maintain stability and functionality. Any miscalculation in the resuspension process can lead to incorrect concentrations, affecting downstream assays such as PCR, qPCR, sequencing, and gene expression studies. Our Oligo Resuspension Calculator eliminates manual errors, helping students and researchers quickly determine the exact solvent volume required to prepare oligos at the desired concentration.
Features of the Tool
Precision and Accuracy
The calculator eliminates the risk of manual calculation errors, ensuring that oligonucleotides are resuspended at the exact molarity required for experiments. This precision is crucial for maintaining data integrity in molecular assays.
User-Friendly Interface
Designed for both students and experienced researchers, the tool provides a clear, step-by-step input process, making it easy to determine the correct resuspension volume without requiring extensive expertise in molarity calculations.
Customization for Modified Oligos
The ability to input a specific molecular weight allows for highly accurate calculations, particularly for chemically modified or fluorescently labeled oligonucleotides, which have different molecular weights than standard DNA sequences.
Time-Saving Automation
Instead of performing complex molarity and volume calculations manually, the calculator instantly generates the required resuspension volume, streamlining laboratory workflows and allowing researchers to focus on their experiments.
Educational Value for Students
For students and early-career researchers, the calculator serves as a learning aid, reinforcing concepts related to oligonucleotide molarity, molecular weight, and concentration preparation. It helps users develop a better understanding of dilution calculations in molecular biology.
Important Considerations When Resuspending Oligonucleotides
Choosing the Right Solvent
The choice of solvent affects oligonucleotide stability and performance in experiments. Common solvents include:
- Nuclease-free water: Suitable for short-term storage and immediate use in molecular assays.
- TE buffer (10 mM Tris, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0): Preferred for long-term storage, as Tris maintains pH stability, and EDTA prevents nuclease degradation.
Ensuring Proper Mixing
After adding the calculated volume of solvent:
- Gently vortex or pipette the solution up and down to promote complete resuspension.
- Avoid vigorous shaking, as it may cause foaming or shearing of longer oligonucleotides.
Managing Temperature Considerations
- Oligonucleotides with high GC content or secondary structures may require gentle heating at 55°C for 5–10 minutes to facilitate complete dissolution.
- RNA oligonucleotides should always be handled in RNase-free conditions to prevent degradation.
Proper Storage Practices
- Short-term storage: Resuspended oligos can be kept at 4°C for a few weeks.
- Long-term storage: For extended stability, store oligos at -20°C or -80°C in aliquots to prevent degradation from repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do I determine the best concentration for resuspension?
The appropriate concentration depends on the application. For PCR, primers are usually resuspended at 100 µM stock concentration, while working dilutions can be 10 µM or lower. Probes for qPCR may require specific concentrations recommended by the manufacturer.
2. What should I do if my oligo does not dissolve completely?
Vortexing and mild heating at 55°C can help dissolve oligos that form aggregates or secondary structures. Ensure the buffer is properly mixed before use.
3. Can I use tap water or distilled water for resuspension?
Only nuclease-free water should be used to avoid degradation caused by contaminants. Distilled water is not recommended as it may contain traces of nucleases.
4. How do I convert an OD260 reading to concentration?
The concentration of an oligo in micrograms per milliliter can be calculated using the formula:
Concentration (µg/mL)=OD260×Dilution Factor×50
For RNA oligos, use 40 instead of 50.
5. How long can resuspended oligos be stored?
Resuspended DNA oligos are stable at -20°C for several months and at -80°C for years. RNA oligos should be stored at -80°C for long-term stability.